Both MoSi2 heating elements and silicon carbide heating elements can be used for high temperature heating. But there are also some differences between these two types of heating elements depending on the application and operating conditions.
Introduction
What is MoSi2 heating element?
MoSi2 heating elements, also known as molybdenum disilicide heating elements, are made from high pure Molybdenum disilicide.

They are characterized by a high melting point and are also stable at high temperatures, which makes them ideal for high-temperature heating applications.
MoSi2 heating elements have a longer service life than other heating elements, which undergo structural changes when heated, increasing their resistance at high temperatures.
What is silicon carbide heating element?
Silicon carbide heating elements are made of selected super quality green silicon carbide as main material.
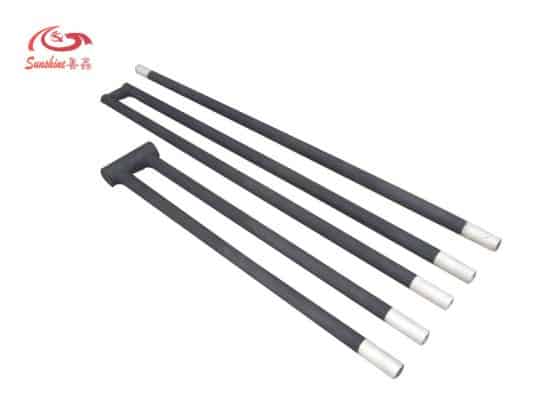

It is characterized by its high stability at high temperatures, high thermal conductivity and fast heating speed. Silicon carbide heating elements are typically used in heating applications that require fast heating and high temperature stability.
Temperature Range
There are also different in the high temperature ranges. MoSi2 heating elements typically have a temperature ranges from 800°C and 1900°C, while silicon carbide heating elements typically have a temperature range from 850°C to 1400°C. Their temperature ranges may change depending on the specific application and operating conditions.
Here is the comparison of the heating temperature ranges of MoSi2 heating elements and silicon carbide heating elements in the form of a table:
| Property | MoSi2 Heating Element | Silicon Carbide Heating Element |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Temperature Range | 800°C to 1900°C | 850°C to 1400°C |
Note: The exact temperature range may vary depending on the specific application and operating conditions.
Operating environments
Another important difference between MoSi2 heating elements and silicon carbide heating elements is their performance in different atmospheres.
MoSi2 heating elements are best used in neutral or reducing atmospheres, as they may have reduced heat transfer efficiency in oxidizing atmospheres due to the formation of an oxide layer on the element surface. Silicon carbide heating elements have oxidation resistance and can be used in both oxidizing and neutral tmospheres.
Service life
The service life of MoSi2 heating elements and silicon carbide heating elements is also highly dependent on the operating environment and application.
MoSi2 heating elements have a longer service life than other heating elements because of the structural changes that occur when they are heated, resulting in increased heat resistance.
Silicon carbide heating elements may have a shorter service life than MoSi2 heating elements, but they are popular for their fast heating speed and high temperature stability, making them suitable for high temperature heating projects where rapid heating is required.
Both MoSi2 heating elements and silicon carbide heating elements are used in high temperature heating applications.
However, they have different temperature ranges, operating environments and service life and are therefore suitable for different applications and operating conditions.
When selecting a heating element, it is important to consider the specific heating requirements of the application, including temperature range, operating atmosphere, and service life, in order to select the most appropriate heating element.