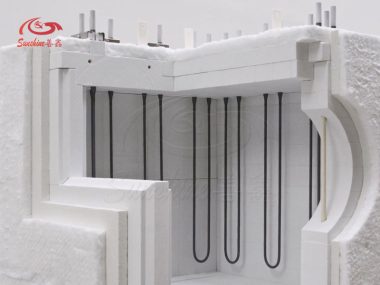
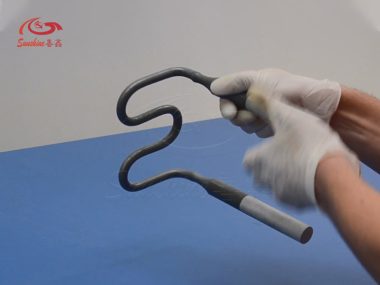
How to design the length of the thermal zone of Mosi2 heating element?
The molybdenum disilicide softens at temperatures over 1200ºC therefore will elongate or stretch when suspende ...
The molybdenum disilicide softens at temperatures over 1200ºC therefore will elongate or stretch when suspende ...
The heating range, thermal conductivity, physical strength and oxidation resistance of SiC and MoSi2 heating elements are different. The heating temperature of SiC heating element is lower than that of Mosi2, but the cost is low. MoSi2 heating element has high thermal efficiency and good oxidation resistance, which is more suitable for high temperature applications
The temperature range of the heating element, the applicable environment, the power requirement, the installation position and the cost are all different, so MoSi2 cannot be used to replace the SiC heating element
The heating element is used for a long time, and there will be dirt, debris and other pollutants on the surface of the heating element. After the power is turned off, the debris can be cleaned and the surface can be maintained to prolong the service life and maintain the heating efficiency.
Silicon carbide heating elements are made of silicon carbide and metal silicon bonded together by a reaction bonding process. Molybdenum disilicide heating element is mainly made of molybdenum and silicon through powder metallurgy process.
When the heating element in an electric furnace fails or is damaged, the heating element needs to be replaced. In this article we will explain in detail how to replace the heating element.
To check the goodness of the heating element, several methods will be used to check the visual inspection, resistance test, on-state test and insulation test.
Choosing a heating element with a suitable size can ensure the efficient operation of the electric furnace and reduce the waste of electric energy.
The silicon-carbon rods are installed with both horizontal and vertical mounting imitation stones. Make sure that the element is not under tension when mounting. There should be enough space to allow the furnace and the element to expand and contract independently.
The replacement of the heating element should be selected according to several conditions such as the power, shape, voltage and working environment of the heating rod. The right heating rod can improve the heating efficiency, extend the service life and save costs
Through the naked eye to observe the heating element and with the help of multimeter and other tools can determine whether the heating element is damaged, such as the need for timely replacement of damaged
Silicon carbide (SiC) heating element is made of high-purity silicon carbide, which is made into a rod-shaped or rolled heating element by pressing silicon carbide powder and then sintering at a high temperature
Electrical heating elements convert the electric current passing through the element into heat energy and radiate the heat, which creates a heating effect.
If the heating element has a decrease in heating capacity, insufficient heat, odor, cracks, gaps or discoloration, etc., it means that the heating element has abnormalities, check the circuit as soon as possible or replace the heating element
Silicon carbide heating elements are made of silicon carbide. MoSi2 heating element is made of high pure molybdenum disilicide.
MoSi2 heating elements and silicon carbide heating elements can both be used for high temperature heating, but there are some differences. I will explain the differences in terms of temperature range, operating conditions and service life.
The temperature range of MoSi2 heating elements is between 1600°C and 1700°C, with special use cases up to 1900°C.
mosi2 heating element is mainly used in ceramic firing industry, electronic components processing industry, glass manufacturing industry, metal processing industry, chemical industry in the drying heating distillation, etc.
Silicon carbide rods are widely used in various high-temperature electric furnaces and other electric heating equipment in the industries of magnetic materials, powder metallurgy, ceramics, glass, metallurgy and machinery.